当前期刊数: 213
ORM(Object relational mappers) 的含义是,将数据模型与 Object 建立强力的映射关系,这样我们对数据的增删改查可以转换为操作 Object(对象)。
Prisma 是一个现代 Nodejs ORM 库,根据 Prisma 官方文档 可以了解这个库是如何设计与使用的。
概述 Prisma 提供了大量工具,包括 Prisma Schema、Prisma Client、Prisma Migrate、Prisma CLI、Prisma Studio 等,其中最核心的两个是 Prisma Schema 与 Prisma Client,分别是描述应用数据模型与 Node 操作 API。
与一般 ORM 完全由 Class 描述数据模型不同,Primsa 采用了一个全新语法 Primsa Schema 描述数据模型,再执行 prisma generate 产生一个配置文件存储在 node_modules/.prisma/client 中,Node 代码里就可以使用 Prisma Client 对数据增删改查了。
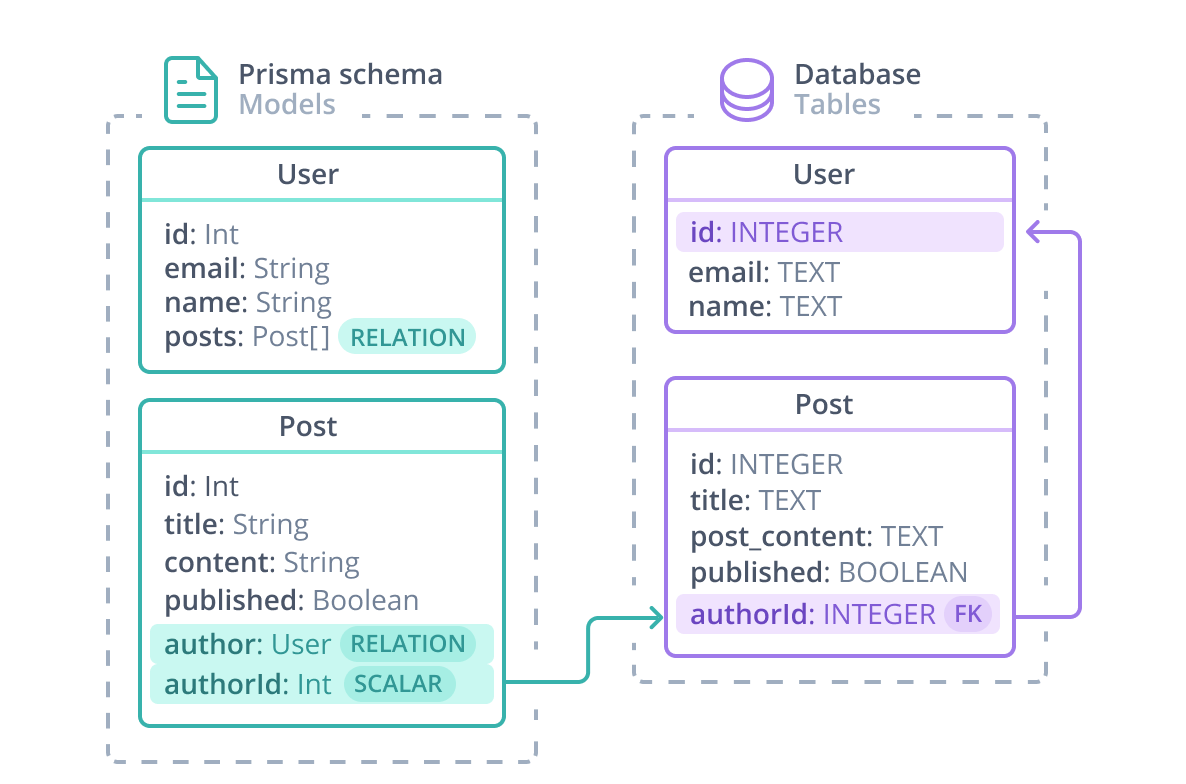
Prisma Schema Primsa Schema 是在最大程度贴近数据库结构描述的基础上,对关联关系进行了进一步抽象,并且背后维护了与数据模型的对应关系,下图很好的说明了这一点:
可以看到,几乎与数据库的定义一模一样,唯一多出来的 posts 与 author 其实是弥补了数据库表关联外键中不直观的部分,将这些外键转化为实体对象,让操作时感受不到外键或者多表的存在,在具体操作时再转化为 join 操作。下面是对应的 Prisma Schema:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 datasource db {
datasource db 申明了链接数据库信息;generator client 申明了使用 Prisma Client 进行客户端操作,也就是说 Prisma Client 其实是可以替换实现的;model 是最核心的模型定义。
在模型定义中,可以通过 @map 修改字段名映射、@@map 修改表名映射,默认情况下,字段名与 key 名相同:
1 2 3 4 5 model Comment {
字段由下面四种描述组成:
字段名。
字段类型。
可选的类型修饰。
可选的属性描述。
1 2 3 model Tag {
在这个描述里,包含字段名 name、字段类型 String、类型修饰 ?、属性描述 @id。
字段类型 字段类型可以是 model,比如关联类型字段场景:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 model Post {
关联场景有 1v1, nv1, 1vn, nvn 四种情况,字段类型可以为定义的 model 名称,并使用属性描述 @relation 定义关联关系,比如上面的例子,描述了 Commenct 与 Post 存在 nv1 关系,并且 Comment.postId 与 Post.id 关联。
字段类型还可以是底层数据类型,通过 @db. 描述,比如:
1 2 3 model Post {
对于 Prisma 不支持的类型,还可以使用 Unsupported 修饰:
1 2 3 model Post {
这种类型的字段无法通过 ORM API 查询,但可以通过 queryRaw 方式查询。queryRaw 是一种 ORM 对原始 SQL 模式的支持,在 Prisma Client 会提到。
类型修饰 类型修饰有 ? [] 两种语法,比如:
1 2 3 4 model User {
分别表示可选与数组。
属性描述 属性描述有如下几种语法:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 model User {
@id 对应数据库的 PRIMARY KEY。
@default 设置字段默认值,可以联合函数使用,比如 @default(autoincrement()),可用函数包括 autoincrement()、dbgenerated()、cuid()、uuid()、now(),还可以通过 dbgenerated 直接调用数据库底层的函数,比如 dbgenerated("gen_random_uuid()")。
@unique 设置字段值唯一。
@relation 设置关联,上面已经提到过了。
@map 设置映射,上面也提到过了。
@updatedAt 修饰字段用来存储上次更新时间,一般是数据库自带的能力。
@ignore 对 Prisma 标记无效的字段。
所有属性描述都可以组合使用,并且还存在需对 model 级别的描述,一般用两个 @ 描述,包括 @@id、@@unique、@@index、@@map、@@ignore。
ManyToMany Prisma 在多对多关联关系的描述上也下了功夫,支持隐式关联描述:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 model Post {
看上去很自然,但其实背后隐藏了不少实现。数据库多对多关系一般通过第三张表实现,第三张表会存储两张表之间外键对应关系,所以如果要显式定义其实是这样的:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 model Post {
背后生成如下 SQL:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 CREATE TABLE "Category" (PRIMARY KEYCREATE TABLE "Post" (PRIMARY KEYCREATE TABLE "CategoryToPost" (integer NOT NULL ,integer NOT NULL ,NOT NULL timestamp NOT NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP ,FOREIGN KEY ("categoryId") REFERENCES "Category"(id),FOREIGN KEY ("postId") REFERENCES "Post"(id)CREATE UNIQUE INDEX "CategoryToPost_category_post_unique" ON "CategoryToPost"("categoryId" int4_ops,"postId" int4_ops);
Prisma Client 描述好 Prisma Model 后,执行 prisma generate,再利用 npm install @prisma/client 安装好 Node 包后,就可以在代码里操作 ORM 了:
1 2 3 import { PrismaClient } from '@prisma/client' const prisma = new PrismaClient ()
CRUD 使用 create 创建一条记录:
1 2 3 4 5 6 const user = await prisma.user .create ({data : {email : 'elsa@prisma.io' ,name : 'Elsa Prisma' ,
使用 createMany 创建多条记录:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 const createMany = await prisma.user .createMany ({data : [name : 'Bob' , email : 'bob@prisma.io' },name : 'Bobo' , email : 'bob@prisma.io' }, name : 'Yewande' , email : 'yewande@prisma.io' },name : 'Angelique' , email : 'angelique@prisma.io' },skipDuplicates : true ,
使用 findUnique 查找单条记录:
1 2 3 4 5 const user = await prisma.user .findUnique ({where : {email : 'elsa@prisma.io' ,
对于联合索引的情况:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 model TimePeriod {
需要再嵌套一层由 _ 拼接的 key:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 const timePeriod = await prisma.timePeriod .findUnique ({where : {year_quarter : {quarter : 4 ,year : 2020 ,
使用 findMany 查询多条记录:
1 const users = await prisma.user .findMany ()
可以使用 SQL 中各种条件语句,语法如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 const users = await prisma.user .findMany ({where : {role : 'ADMIN' ,include : {posts : true ,
使用 update 更新记录:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 const updateUser = await prisma.user .update ({where : {email : 'viola@prisma.io' ,data : {name : 'Viola the Magnificent' ,
使用 updateMany 更新多条记录:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 const updateUsers = await prisma.user .updateMany ({where : {email : {contains : 'prisma.io' ,data : {role : 'ADMIN' ,
使用 delete 删除记录:
1 2 3 4 5 const deleteUser = await prisma.user .delete ({where : {email : 'bert@prisma.io' ,
使用 deleteMany 删除多条记录:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 const deleteUsers = await prisma.user .deleteMany ({where : {email : {contains : 'prisma.io' ,
使用 include 表示关联查询是否生效,比如:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 const getUser = await prisma.user .findUnique ({where : {id : 19 ,include : {posts : true ,
这样就会在查询 user 表时,顺带查询所有关联的 post 表。关联查询也支持嵌套:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 const user = await prisma.user .findMany ({include : {posts : {include : {categories : true ,
筛选条件支持 equals、not、in、notIn、lt、lte、gt、gte、contains、search、mode、startsWith、endsWith、AND、OR、NOT,一般用法如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 const result = await prisma.user .findMany ({where : {name : {equals : 'Eleanor' ,
这个语句代替 sql 的 where name="Eleanor",即通过对象嵌套的方式表达语义。
Prisma 也可以直接写原生 SQL:
1 2 3 4 const email = 'emelie@prisma.io' const result = await prisma.$queryRaw(Prisma .sql `SELECT * FROM User WHERE email = ${email} `
中间件 Prisma 支持中间件的方式在执行过程中进行拓展,看下面的例子:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 const prisma = new PrismaClient ()async (params, next) => {console .log (params.args .data .title )console .log ('1' )const result = await next (params)console .log ('6' )return resultasync (params, next) => {console .log ('2' )const result = await next (params)console .log ('5' )return resultasync (params, next) => {console .log ('3' )const result = await next (params)console .log ('4' )return resultconst create = await prisma.post .create ({data : {title : 'Welcome to Prisma Day 2020' ,const create2 = await prisma.post .create ({data : {title : 'How to Prisma!' ,
输出如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 Welcome to Prisma Day 2020
可以看到,中间件执行顺序是洋葱模型,并且每个操作都会触发。我们可以利用中间件拓展业务逻辑或者进行操作时间的打点记录。
精读 ORM 的两种设计模式 ORM 有 Active Record 与 Data Mapper 两种设计模式,其中 Active Record 使对象背后完全对应 sql 查询,现在已经不怎么流行了,而 Data Mapper 模式中的对象并不知道数据库的存在,即中间多了一层映射,甚至背后不需要对应数据库,所以可以做一些很轻量的调试功能。
Prisma 采用了 Data Mapper 模式。
ORM 容易引发性能问题 当数据量大,或者性能、资源敏感的情况下,我们需要对 SQL 进行优化,甚至我们需要对特定的 Mysql 的特定版本的某些内核错误,对 SQL 进行某些看似无意义的申明调优(比如在 where 之前再进行相同条件的 IN 范围限定),有的时候能取得惊人的性能提升。
而 ORM 是建立在一个较为理想化理论基础上的,即数据模型可以很好的转化为对象操作,然而对象操作由于屏蔽了细节,我们无法对 SQL 进行针对性调优。
另外,得益于对象操作的便利性,我们很容易通过 obj.obj. 的方式访问某些属性,但这背后生成的却是一系列未经优化(或者部分自动优化)的复杂 join sql,我们在写这些 sql 时会提前考虑性能因素,但通过对象调用时却因为成本低,或觉得 ORM 有 magic 优化等想法,写出很多实际上不合理的 sql。
Prisma Schema 的好处 其实从语法上,Prisma Schema 与 Typeorm 基于 Class + 装饰器的拓展几乎可以等价转换,但 Prisma Schema 在实际使用中有一个很不错的优势,即减少样板代码以及稳定数据库模型。
减少样板代码比较好理解,因为 Prisma Schema 并不会出现在代码中,而稳定模型是指,只要不执行 prisma generate,数据模型就不会变化,而且 Prisma Schema 也独立于 Node 存在,甚至可以不放在项目源码中,相比之下,修改起来会更加慎重,而完全用 Node 定义的模型因为本身是代码的一部分,可能会突然被修改,而且也没有执行数据库结构同步的操作。
如果项目采用 Prisma,则模型变更后,可以执行 prisma db pull 更新数据库结构,再执行 prisma generate 更新客户端 API,这个流程比较清晰。
总结 Prisma Schema 是 Prisma 的一大特色,因为这部分描述独立于代码,带来了如下几个好处:
定义比 Node Class 更简洁。
不生成冗余的代码结构。
Prisma Client 更加轻量,且查询返回的都是 Pure Object。
至于 Prisma Client 的 API 设计其实并没有特别突出之处,无论与 sequelize 还是 typeorm 的 API 设计相比,都没有太大的优化,只是风格不同。
不过对于记录的创建,我更喜欢 Prisma 的 API:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 const userRepository = getManager ().getRepository (User )const newUser = new User ()name = 'Alice' save (newUser)const userRepository = getManager ().getRepository (User )insert ({name : 'Alice' ,const user = User .build ({name : 'Alice' ,await user.save ()const user = await User .create ({name : 'Alice' ,email : 'alice@prisma.io' ,const newUser = await prisma.user .create ({data : {name : 'Alice' ,
首先存在 prisma 这个顶层变量,使用起来会非常方便,另外从 API 拓展上来说,虽然 Mongoose 设计得更简洁,但添加一些条件时拓展性会不足,导致结构不太稳定,不利于统一记忆。
Prisma Client 的 API 统一采用下面这种结构:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 await prisma.modelName .operateName ({data : ,where : ,
所以总的来说,Prisma 虽然没有对 ORM 做出革命性改变,但在微创新与 API 优化上都做得足够棒,github 更新也比较活跃,如果你决定使用 ORM 开发项目,还是比较推荐 Prisma 的。
在实际使用中,为了规避 ORM 产生笨拙 sql 导致的性能问题,可以利用 Prisma Middleware 监控查询性能,并对性能较差的地方采用 prisma.$queryRaw 原生 sql 查询。
讨论地址是:精读《Prisma 的使用》· Issue ##362 · dt-fe/weekly
如果你想参与讨论,请 点击这里 ,每周都有新的主题,周末或周一发布。前端精读 - 帮你筛选靠谱的内容。
关注 前端精读微信公众号
版权声明:自由转载-非商用-非衍生-保持署名(创意共享 3.0 许可证 )